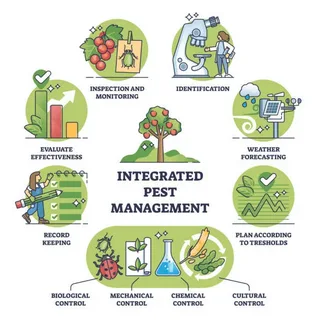
Introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings, which prey on harmful organisms. This biological approach encourages a balanced ecosystem within your plant beds.
Utilize companion planting, combining species that deter harmful invaders. For instance, marigolds can repel nematodes, serving as a natural barrier against damage in vegetable patches.
Implement barriers such as row covers or nets to physically block harmful species. These protective measures keep threats at bay without the need for chemical interventions.
Regularly monitor your flora for signs of infestation. Early detection allows for targeted treatments, such as neem oil or insecticidal soap, which offer a less toxic alternative compared to conventional pesticides.
Embrace the power of natural repellents made from garlic or hot peppers. Spraying diluted solutions can effectively deter unwanted visitors without harming beneficial insects.
By integrating these techniques into your horticultural routine, a thriving environment for your plants can be established while minimizing reliance on synthetic chemicals.
Identifying Common Garden Pests and Their Signs
Regular observation is key to noticing the presence of unwanted creatures in your plants. Look for chewed leaves, discolored patches, or wilting as indicators of potential infestations.
Aphids
Aphids are small, soft-bodied insects often found in clusters on new growth. Their presence can result in curled or distorted leaves. Stickiness on surfaces beneath infested plants may indicate honeydew excreted by these pests.
Spider Mites
Spider mites are tiny and often go unnoticed until significant damage occurs. Yellow or stippled leaves, along with fine webbing between stems and undersides of leaves, signal their invasion.
Regularly inspecting your flora for these signs aids in early detection and remediation. Utilizing natural solutions can help in managing these nuisances effectively. For tools and resources that can enhance your control methods, visit All tools for you.
Using Companion Planting to Deter Insects
Integrate specific plants that repel unwanted insects. Marigolds are known for deterring nematodes and aphids. Plant them alongside vegetables such as tomatoes and peppers for optimal results.
Effective Combinations
- Basil: Grows well with tomatoes, repelling flies and mosquitoes.
- Garlic: Plant near roses to protect against aphids and spider mites.
- Nasturtiums: Attract aphids away from essential crops, serving as a trap plant.
- Mint: Penetrates limited areas; use it to repel ants and cabbage moths when placed around cabbage family crops.
Beneficial Insects Attraction
Encourage pollinators and pest-controlling insects by including flowers like dill and fennel. These plants not only foster biodiversity but also create an ecosystem that can manage harmful insects efficiently.
- Linda’s Lemon (Dill): Attracts ladybugs and lacewings.
- Yarrow: Draws predatory wasps that hunt aphids.
This method reduces reliance on chemical treatments, creating a balanced environment conducive to plant health.
Creating Homemade Natural Repellents for Your Plants
Combine one quart of water with two tablespoons of liquid soap and one tablespoon of cayenne pepper or crushed garlic for an effective spray. This mixture targets soft-bodied insects and deters them while remaining safe for beneficial bugs.
Garlic and Pepper Spray
Blend a whole bulb of garlic and one tablespoon of cayenne pepper with a quart of water. After straining, fill a spray bottle and apply it directly to affected areas. This concoction not only repels insects but also enhances the aroma of your plants, making them less attractive to unwanted visitors.
Neem Oil Solution
Mix two teaspoons of neem oil with a gallon of water. Spray this on plants every two weeks to disrupt the life cycle of harmful insects. Neem oil acts as a deterrent and can prevent larvae from maturing into adult insects. For more tips and resources, visit Tommy for Wisconsin.
Attracting Beneficial Insects to Control Pest Populations
Plant a diverse array of flowering species, particularly those that bloom at different times, ensuring a continuous food supply for helpful insects like pollinators and predators of harmful insects. Species such as marigolds, dill, fennel, and yarrow are excellent choices, attracting ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps.
Creating Habitats
Provide nesting sites and shelter by incorporating native plants, grasses, and a variety of foliage into the space. Adding small stones, twigs, or brush piles can create a refuge for beneficial insects, encouraging their presence in the area.
Water Sources
Include shallow water dishes with small stones or pebbles that allow insects to drink without drowning. Regularly refresh these sources to maintain their usefulness and attract more beneficial wildlife.
Maintaining an ecosystem that naturally balances insect populations minimizes reliance on chemical interventions. For more insights on gardening tools and resources, visit Garden Machinery Hub.